For printing companies and equipment manufacturers, a longstanding challenge exists in maintaining color consistency from digital proofing to printing presses, between different printing machines, and even across different production facilities. While equipment manufacturers strive for shelf consistency, printing companies face challenges in color stability due to different devices, operators, and even production locations. Therefore, in today’s fast-paced and high-demand production environment, developing workflows and building reliable control methods to achieve color matching across multiple locations or devices is crucial for enhancing the production quality and efficiency of printing factories.
Application and Current State of Color Management
The past decade has witnessed rapid development in color management technology in China. We have evolved from not understanding G7 certification to cultivating over thirty in-house G7 experts, enabling each production facility to independently complete G7 certification and annual renewals. We have transitioned from being unfamiliar with single-point density meters to equipping each printing press with color scanning systems to track printing color changes, guiding mass production. Despite the gradual complexity of our production control processes and the increasing number of supporting tools and methods, the challenge of color instability still persists.
We attempted continuous printing of 4000 sample sheets, sampling every 100 sheets, tracking and monitoring gray balance color patches at two different locations, and recording measurement values. The color scanning system can track changes in printing color, guiding machine operators to adjust ink keys accordingly to correct colors. While this meets production requirements to some extent, the lag and accuracy limitations of manual adjustments have prevented achieving the desired color consistency control throughout the entire printing process.
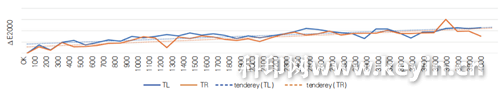 In response to the inherent instability of printing colors in recent years and to reduce the subjective impact of operators on production process control, we began developing and applying closed-loop automatic color correction technology through digitization to automate and intelligentize the production process.
In response to the inherent instability of printing colors in recent years and to reduce the subjective impact of operators on production process control, we began developing and applying closed-loop automatic color correction technology through digitization to automate and intelligentize the production process.
Development and Application of Closed-Loop Automatic Color Correction Technology
Currently, there are various closed-loop automatic color correction solutions in the industry, including original equipment configurations on printing machines or third-party technical solutions. Third-party technical solutions have more user-friendly and adaptable designs that can be updated iteratively based on user needs. However, they may have compatibility issues with printing machine systems, especially with newer printing machine systems. While original equipment configurations eliminate compatibility problems, they are expensive, have low market usage rates, and their system interfaces and functionalities may lack user testing and optimization updates, resulting in less-than-ideal user experiences.
There is no inherent good or bad in technical solutions; one should choose the preferred solution that suits their needs. It is crucial to emphasize that the closed-loop automatic color correction system, unlike other color management software and hardware devices, does not immediately function after installation. The system has self-learning capabilities, adjusting and correcting control curves based on the different states of the printing press and the type of substrate during usage. It can also optimize CIP3 data for more accurate ink pre-setting. When used correctly, the accuracy and efficiency of the closed-loop automatic color correction system increase over time. However, improper use may render the system ineffective and even abandoned during the system’s self-learning phase.
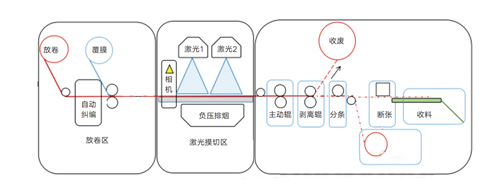
The closed-loop automatic color correction system consists of two main parts: printing color scanning and tracking, and printing color closed-loop correction. The functions of printing color scanning and tracking were implemented ten years ago, with almost all printing presses at Yutong equipped with automatic color scanning systems capable of reading color information from printed sheets. Subsequently, machine operators manually adjusted ink keys based on the readings to achieve color correction throughout the entire mass production process. Currently, we have implemented the second part, i.e., printing color closed-loop correction. The closed-loop automatic color correction system works through four cyclic steps, as shown in Figure 2.
 (1) Before printing starts, the system presets the initial ink quantity on the ink fountain based on pre-press CIP3/CIP4 pre-inking data. After preparation, the printing press starts running, and once the ink quantity is in place, a printed sheet is extracted. The scanner reads the color strip, displaying color density data for each ink zone and identifying areas where ink density data exceeds the tolerance range.
(1) Before printing starts, the system presets the initial ink quantity on the ink fountain based on pre-press CIP3/CIP4 pre-inking data. After preparation, the printing press starts running, and once the ink quantity is in place, a printed sheet is extracted. The scanner reads the color strip, displaying color density data for each ink zone and identifying areas where ink density data exceeds the tolerance range.
(2) The closed-loop automatic color correction system obtains the scanned color data and calculates the adjustment amounts for each ink key corresponding to different color groups based on the differences between the current density and the set target.
(3) The closed-loop automatic color correction system generates ink control information according to the calculation results and transfers it to the printing press system. It automatically adjusts the ink key openings for each color group precisely, thereby adjusting the ink amount to control the density of each color ink.
(4) After the closed-loop automatic color correction system completes the automatic adjustment of the ink keys, the printing press runs again. Once the ink quantity is in place, a printed sheet is extracted, and the scanner reads the color strip, displaying color density data for each ink zone. The results show that the data for each color ink zone is back within the tolerance range, indicating stabilized color.
The above steps are simplified, and in actual production, it may take several cycles to achieve stable color. This is related to factors such as the self-learning state of the closed-loop automatic color correction system, the accuracy of the system curve, and the stability of materials.
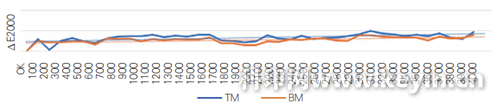
As a comparison, we reprinted 4000 sample sheets using the closed-loop automatic color correction system, sampling every 200 sheets, tracking and monitoring gray balance color patches at two different locations. The recorded measurement values show color deviation as presented in Figure 3. Compared to manual adjustment of ink keys by machine operators, the closed-loop automatic color correction system demonstrates excellent color deviation performance, with minimal color fluctuation and significantly improved batch color stability during mass production.
Click to learn more about book printing, sticker printing, medicine box, hardcover book printing, PE bag, Religious book printing, shopping bag printing, catalog printing, and printing in China.
 In traditional printing processes, manual extraction of printed sheets is required to check colors and adjust ink keys. After data and intelligent optimization of the printing process, the closed-loop automatic color correction system reduces human factors during production, achieving color stability control. Simultaneously, it shortens printing preparation time, improves production efficiency, and ensures color communication uniformity throughout the entire printing workflow and packaging supply chain.
In traditional printing processes, manual extraction of printed sheets is required to check colors and adjust ink keys. After data and intelligent optimization of the printing process, the closed-loop automatic color correction system reduces human factors during production, achieving color stability control. Simultaneously, it shortens printing preparation time, improves production efficiency, and ensures color communication uniformity throughout the entire printing workflow and packaging supply chain.
Printing, as one of the Four Great Inventions of ancient China, has evolved through the wisdom and efforts of predecessors. Technical inheritance is our primary task and crucial mission. In today’s era of rapid scientific and technological development, combining technological forces with traditional skills on the foundation of inheritance is the sustainable approach. Striving for excellence in intelligent manufacturing is the long-term plan. We look forward to seeing more successful applications of intelligent manufacturing solutions in the printing industry.
Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to react!